Table of Contents
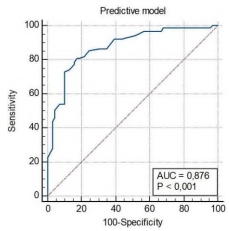
Background: Improving the accuracy of axillary lymph node (ALN) status assessment and the search for new markers associated with the risk of breast cancer (BC) metastasis continues to be an urgent problem. Aim: To establish the prognostic significance of the expression of PD-L1 in a tumor for assessing the risk of BC metastasis in ALNs. Materials and methods: A retrospective, case‒control cohort study included 158 patients aged 30 to 85 years with newly diagnosed BC. The material for the study was tumor samples obtained by trephine biopsy. The expression of PD-L1 in the tumor was studied on the invasive component of puncture biopsy specimens by immunohistochemistry using PD-L1 polyclonal antibodies. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistica 12.0 software. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for PD-L1 and Ki67 were constructed to discriminate cases with and without metastases in the ALNs. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to establish independent predictors associated with the risk of BC metastasis. A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results: According to the results, independent predictors of a high risk of BC regional metastasis were T2 (OR = 5.81, 95% CI = 1.75–19.35, p = 0.004) and T3-4 (OR = 43.07, 95% CI = 9.31–199.2, p < 0.0001) stages of BC, absence of an intraductal component (OR = 3.68, 95% CI = 1.32–10.33, p = 0.013), presence of lymphovascular invasion (OR = 3.32, 95% CI = 1.34–8.22, p = 0.009), luminal B HER2-positive (OR = 6.82, 95% CI = 1.13–42.26, p = 0.036) and triple negative (OR = 8.52, 95% CI = 1.12–64.89, p = 0.038) molecular biological subtypes of BC, and PD-L1 expression coefficient greater than 1.65 (OR = 6.39, 95% CI = 2.54–16.09, p = 0.0001). Based on the data obtained, an original noninvasive method for assessing a high risk of BC regional metastasis was developed, the sensitivity of which was 80.9%, the specificity - 82.6%, and the accuracy - 85.7%. The area under the curve (AUC) was 0.876 (95% CI = 0.818–0.924, р < 0.0001). Conclusion: The results of the study indicate that the assessment of PD-L1 expression in a tumor can improve the accuracy of predicting the risk of regional BC metastasis.
Studying vitamin E’s antioxidant capabilities and how they relate to oxidative enzymes in the context of ovarian cancer was the focus of this study. A case-control study was conducted, with 100 women with ovarian cancer serving as cases and 30 women in good health serving as controls. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to assess serum levels of trypsin, chymotrypsin, pancreatic-type amylase, and vitamin E, while the dimercaptopropanol tributyrate (BALB) method was used to measure lipase levels. Patients with ovarian cancer were shown to have lower levels of chymotrypsin and lipase and higher levels of trypsin and amylase than controls. The two groups had almost the same vitamin E content. According to these findings, oxidative enzymes may have a role in the progression of ovarian cancer by increasing trypsin and amylase and decreasing chymotrypsin and lipase. Although vitamin E was thought to slow the development of gynecologic malignancies, the study found no such impact. Further research with larger study groups is necessary to obtain more robust results.
Objectives: To describe the prevalence, characteristics, and outcomes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) associated interstitial lung disease (ILD) in a multi‐centre cohort. Methods: We collected data from 132 patients with RA prospectively over a four‐year period. Baseline socio‐demographic characteristics (age, sex, smoking status, disease duration, time to diagnosis) were obtained. Patients were also assessed clinically to determine articular disease activity as well as to identify any respiratory involvement. Baseline chest radiographs were requested for all participants and those with findings suggestive of possible lung disease underwent high‐resolution computed tomography (HRCT) to assess whether ILD was present. All patients with confirmed ILD were given rituximab monotherapy at recommended doses. Results: From a cohort of 132 adult RA patients, four were found to have RA‐ILD on HRCT giving a prevalence of 3%. They had a mean age of 55 ± 18.5 years with three of them being female. They had long standing RA with significant delay in time to diagnosis. None of our patients were smokers but all were strongly seropositive. Non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) was diagnosed in two patients while usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) was diagnosed in the remaining two. All patients benefitted from rituximab monotherapy as evidenced by improvement in respiratory symptoms, combined with non-progression on repeat HRCT, in tandem with clinical disease activity scores. Conclusion: Although our patient numbers were small, our paper describes epidemiological differences in RA‐ILD for our patients when compared with patients in the West. Rituximab showed promising results in our patients, but results must clearly be interpreted with caution.
Background: Our study aimed to determine the frequency of microsatellite instability (MSI) and characterize the associations between MSI status, PD-L1 expression, and clinicopathological features in Vietnamese patients with gastric cancer. Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study that analyzed 87 patients with gastric cancer who underwent gastrectomy from January 2020 to March 2023. MSI status was assessed by immunohistochemistry for mismatch repair proteins. PD-L1 expression was evaluated by tumor proportion score (TPS) and combined positive score (CPS). Associations between MSI, PD-L1, and clinicopathologic factors were analyzed. Results: MSI-high (MSI-H) was identified in 13.8% of tumors and significantly associated with intestinal subtype, moderate differentiation, necrosis, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and PD-L1 positivity. Lymphatic invasion correlated with increased TPS. Intestinal classification correlated with higher CPS. Conclusion: MSI-H identifies a subset of gastric cancers with distinct features. PD-L1 expression is associated with aggressive disease parameters. Biomarker-based stratification may guide personalized therapy.
Breast cancer (BC) is a prevalent malignancy among women, ranking as the second most commonly diagnosed cancer globally. Notably, a substantial proportion of breast cancer-related fatalities, up to 90 percent, are attributed to the development of distant organ metastases. While Cadherin1 (CDH1) has conventionally been considered a tumor-suppressor gene in cancer research, recent investigations have unequivocally revealed that both CDH1 and its encoded E-cadherin exhibit oncogenic characteristics. The primary focus of this case-control study is to ascertain the involvement of the CDH1 gene in a specific subset of Iraqi female patients. A total of ninety patients sought diagnosis and treatment at the Oncology Teaching Hospital in Medical City and the Oncology Unit at Al-Yarmouk Teaching Hospital in Baghdad. In addition, we included 30 apparently healthy individuals as blood control subjects and another 30 women with benign breast tumors as tissue control subjects for the study. In the initial phase of the study, we conducted a serological analysis using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect the concentration of E-cadherin in serum samples from two groups of BC patients. The group with locally advanced and metastatic BC exhibited a significantly higher E-cadherin concentration (963.4 ± 89.8 pg/mL) compared to the group with localized BC. In the second part of the research, qRT-PCR was performed to analyze the expression of the CDH1 gene across all sample types. CDH1 was shown to have the greatest fold expression (2.550 ± 0.164) in cases with locally progressed and metastatic BC. Compared to the seemingly healthy control group, the fold expression for localized BC was 1.456 ± 0.055, and for malignant tissue it was 1.886 ± 0.08621. In conclusion, this study provides compelling evidence supporting CDH1 as an oncogene in BC. The significance of CDH1 in BC tumorigenesis underscores its potential for the development of novel detection biomarkers and targeted therapeutic approaches for BC treatment. Notably, CDH1 exhibited elevated expression levels in BC tissues and demonstrated an association with an unfavorable distant metastasis-free survival outcome.
We aimed to evaluate the association of HLA DRB1 and DQB1 alleles with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and to investigate their relationship with anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPA) and RA severity. We performed a case-control study of 81 RA patients compared with 100 healthy controls. Sociodemographic data, disease activity scores, functional impact, structural damage, ACPA, rheumatoid factor (RF), and HLA DRB1 and DQB1 alleles were determined. Forty-six patients expressed HLA DRB1, predominantly DRB1*04. These alleles were more frequent in RA patients than in controls. DRB1*04:05 was the most associated allele with RA susceptibility, 54.5% of RF-positive patients expressed DRB1*04:05 with a significant correlation. Similarly, a highly significant association with DRB1*15:01 and RF positivity was found. DRB1*01:01, 04:05, 11:01, and 15:01 were associated with the presence of ACPA. Patients with DRB1 alleles had more extraarticular manifestations (EAM). Multivariate analysis concluded that DRB1*04:05 was only associated with ACPA positivity. Regarding DQB1, DQB1*03:02 was the most associated with RA. DQB1*02:01, 03:01, 03:02, 05:01, and 06:01 were associated with RF-positive RA. DQB1*06:01 was associated with ACPA. Only HLA DQB1*02:01 and 06:01 were associated with the presence of EAM. DAS28 was reduced in the presence of DQB1. HAQ > 0.5 were correlated with DQB1 alleles. In addition, there was more structural damage in RA encoding for DQB1. In linear regression, DQB1*06:01 were associated with RF positivity, but there was no association with the other parameters. Our study confirmed that DRB1 and DQB1 expression was significantly associated with ACPA, increased HAQ, increased sharp score, and the presence of EAM.
Objectives: To synthesize and evaluate the anti-inflammatory potential of fifteen naphthoquinones (NQs), determining their ability to inhibitory nitric oxide (NO•) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production. Methods: NQs were screened for their inhibitory effect on NO• and PGE production using LPS-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Results: Three linear furanonaphthoquinones (4-6) were identified as potent inhibitors of NO• and PGE2 production, with IC50 values ranging from 0.45 to 2.86 μM (NO•) and 0.38 to 1.65 (PGE2), highlighting the potent activity showed by compound 5 with IC50 values lower than one and high selectivity indices. Conclusions: Synthesized furanonaphthoquinones constitute leading compounds for the design of new anti-inflammatory agents and provide a valuable tool for designing new NQs that might be useful to treat inflammation. The evaluation of compounds 4-6 using in vivo models is warranted.
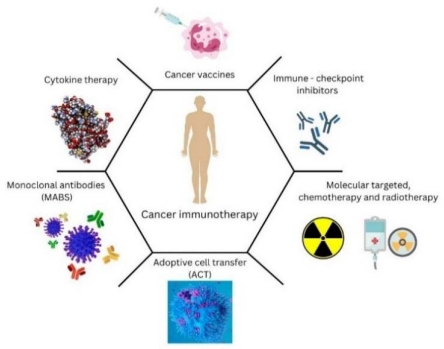
Chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and surgery are recognized as the main treatment modalities for cancer. These therapeutic strategies may be effective in the early stages of the disease but are usually ineffective in advanced stages or when the cancer recurs. Recently, great efforts have been made to understand the complex interaction between the immune system and its surveillance of cancer and to find effective immunotherapies for all stages of cancer. Several types of immunotherapies, including adoptive immunotherapy, cancer vaccines, and immune checkpoint blockades, are receiving considerable attention. The clinical relevance of T lymphocytes and NK cells in combating carcinomas is beyond doubt, but their mechanism of tumor surveillance is far from being fully understood. In this review, much attention has been paid to the complex interplay between T lymphocytes, NK cells, and cancer cells and their role in immunotherapy. Moreover, in this review, we summarized the current data on cancer immunotherapies, especially cancer vaccines, T- and NK cell-based immunotherapies. In addition, we highlighted the role of biomarkers as important indicators of response to immunotherapy, as well as potential problems and solutions related to immunotherapy. Insights into the future of immunotherapy are also presented in this review.
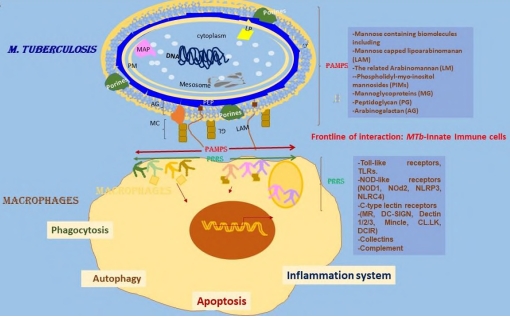
Tuberculosis (Tb) is still a global health problem, especially in developing countries. Several factors contribute to this, among them the increasing multidrug resistance strains, the dangerous liaisons with other intracellular pathogens, such as HIV, and more recently, SARS-CoV2 pandemics. There are many aspects that remain to understand the bacterial molecular mechanism of pathogenicity and the immune response induced by the interaction of M. tuberculosis (MTb) with the host. The official and current vaccine based on the attenuated Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG) is protective against several forms of Tb meningitis and Miliary TB or disseminated disease in young children. However, it fails to protect young and adult individuals. There are several new promising candidates for vaccines to replace or boost BCG-induced immunity. Several evidences exist from humans and mice on the role of the trained innate memory of monocytes and NK cells, on the second encounter with the same mycobacterial pathogen or other respiratory pathogens. This type of immune response is nonspecific and independent of the T and B cells. Thus, BCG vaccination is a double immunogen that activate specific immune responses and is also able to stimulate nonspecific immune responses. Here, it is outlined the host immunity against MTb, the potential of BCG vaccination and prime boost protocols for routing innate and adaptive immune responses in TB.
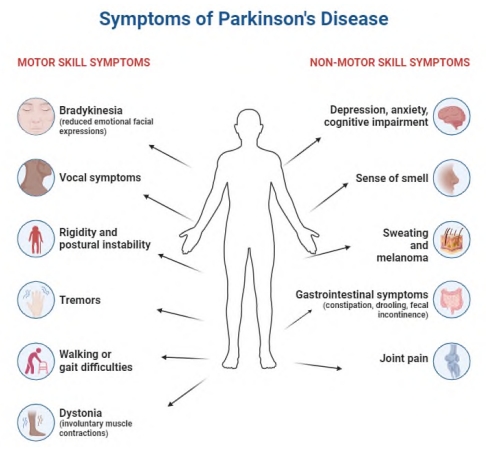
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the accumulation of misfolded proteins and impaired protein degradation mechanisms. Dysregulation of protein degradation processes, including autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome system, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of PD. Recently, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool to enhance our understanding of protein degradation in PD. This abstract provides an overview of the advancements in studying protein degradation in PD with the aid of AI. The integration of AI techniques, such as machine learning and data mining, has enabled the identification and characterization of protein degradation pathways involved in PD. By analyzing large-scale protein-protein interaction networks, AI algorithms have revealed key interactions and pathways underlying protein degradation dysfunction in PD. Furthermore, AI models can predict the efficiency of protein degradation processes and identify potential targets for enhancing protein degradation in PD, aiding in the development of novel therapeutic interventions.AI-based approaches have also been instrumental in drug discovery and target identification, as they can screen vast databases of compounds to identify potential drugs or small molecules that modulate protein degradation pathways relevant to PD. Additionally, deep learning algorithms have facilitated the analysis of protein structures, predicting protein stability and folding patterns that impact protein degradation. Moreover, AI has played a crucial role in the identification of protein biomarkers associated with protein degradation dysfunction in PD. These biomarkers can aid in early diagnosis and monitoring of the disease, enabling timely intervention and personalized treatment strategies. The advancements presented in this abstract highlight the transformative potential of AI in elucidating the intricate mechanisms of protein degradation in PD. Collaborations between AI researchers, biologists, and clinicians are essential to translate these findings into effective diagnostic tools and therapeutic interventions for PD patients.
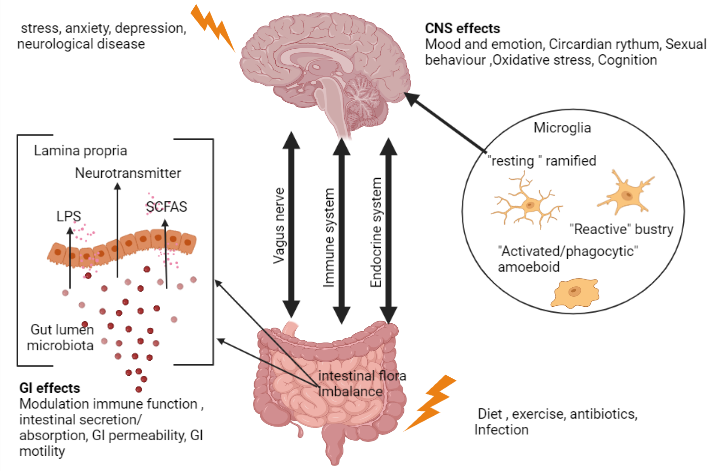
The “gut-brain axis” or “brain-gut axis” communication mechanism has a bidirectional approach because it depends on showing top-down or bottom-up channels to function. It is one of the few systems in the body that combines neuronal routes with humoral pathways, which include cytokines, hormones, and neuropeptides as chemical messages. It was also discovered to be diverse because it contains spinal, vagus, sympathetic, and intestinal nerves. The role of microbes as signaling agents in the gut-brain axis has been proven by the most recent research, which is primarily based on animal models. Probiotics are living bacteria that improve one’s health when ingested in large enough doses. Gut microbes are suspected to play a role in a variety of psychiatric disorders, making them a potential therapeutic target. The stomach and the brain are linked via a two-way communication pathway called the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Current interventional research on probiotics and the gut-brain axis has been evaluated for its findings in the treatment of depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. Neuropathic pain is brought on by a lesion or injury to the nerve system, which is further demonstrated by a malfunction of the somatosensory system. Such a developed form of pain affects both peripheral and central nervous system neurons. According to research, probiotics can enhance the gut’s dynamic environment and are good for both the gut and the brain. Therefore, the focus of this review is on how probiotics, the microbiota-gut-brain axis, and the gut-brain axis relate to neuropathic pain.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led to an urgent need for vaccine development and global distribution. Recent research suggests that there may be potential impacts on the central nervous system (CNS), as evidenced by findings from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This article aims to provide feedback on the current evidence regarding the associations between COVID-19 vaccination and neurological complications. It is essential to conduct further research to enhance our scientific understanding of how vaccines interact with the central nervous system. This knowledge can significantly support public health efforts in controlling the spread of new viral variants through widespread vaccination.
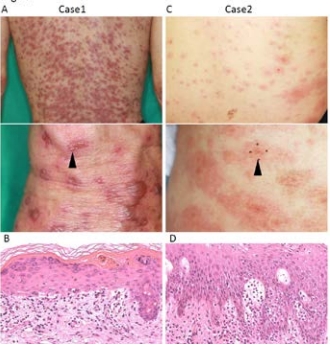
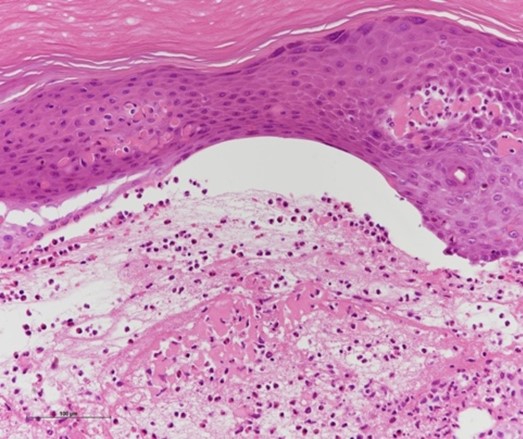
COVID-19 is a pandemic involving severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which started in China at the end of 2019 and has spread globally. Among COVID-19 patients, 17.8% are under 20 years of age. Most children infected with SARS-CoV-2 are asymptomatic or only oligosymptomatic and can easily be overlooked. We followed an 11-year-old boy showing exudative erythema multiforme, which appeared during isolation at home following a positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for COVID-19. Our case, although otherwise asymptomatic, showed typical clinical and histological manifestations of the erythema multiforme-like lesions associated with COVID-19. The presence of such an asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 carrier who developed erythema multiforme-like skin lesions provides the possibility that some undefined infectious organisms, such as SARS-CoV-2, could be the origin of exudative erythema multiforme cases without any apparent cause.
The COVID-19 pandemic has increased mRNA vaccine usage and revealed various cutaneous adverse events, such as injection site reactions, urticaria, and morbilliform eruptions. Multiple centers have reported erythema multiforme (EM) as a COVID-19 vaccine-associated adverse event. Our center observed two cases of EM in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) after COVID-19 vaccination. Notably, ICI administration is known to cause cutaneous adverse events, including EM. A previous report indicated that administering COVID-19 vaccination to patients receiving ICI treatment could promote severe systemic symptoms. This raise concerns that COVID-19 vaccination might rapidly worsen skin rashes in these patients. Our report demonstrates that skin rash related to COVID-19 vaccine-induced EM in ICI-treated patients does not significantly differ from that of COVID-19 vaccine-related EM. Additionally, in both cases, the skin rash resolved without exacerbation. Further research is necessary to determine optimal management strategies. However, our findings provide reassurance that COVID-19 vaccination is safe in ICI-treated patients and should not be avoided.
Pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) is a rare neutrophilic dermatosis with multiple different clinical presentations and associated comorbidities. It often presents as ulcerated lesions with a violet/erythematous border and an irregular undercut margin. In this largest single-centre case series study in Antalya-Turkey, we reviewed 32 PG patients diagnosed consecutively within the last 5-year period. Consistent with the literature, PG morphologically often presented with the ulcerative clinic (90.6%), and inflammatory bowel disease (15.6%) was the most common etiologic factor. In our study, female gender predominance (78.2%), lower extremity localization (93.7%), and the rate of multiple ulcers at diagnosis (90.6%) were more prominent than in the literature. Unlike the literature, oral mucosa involvement and syndromic form (both, 6.2%) of the disease were detected more frequently. Our results indicate that PG patients may show differences according to geographical and ethnic differences and/or characteristics of the healthcare institution.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as nivolumab, which target anti‐programmed cell death-1 (PD-1), have been applied to a variety of cancers and have caused immune‐related adverse events (irAEs). Although an association between ICIs and bullous pemphigoid and mucosal pemphigoid (MMP) has been reported, the complex mechanisms underlying PD-1 inhibition‐induced autoantibody production and autoimmunity remain unelucidated. In this report, we present a unique case of MMP involving the palmoplantar lesions during adjuvant nivolumab therapy. A Japanese woman in her 70s was treated with nivolumab for postoperative vulvar malignant melanoma; after the 12th cycle of treatment, ulcers were seen in the oral cavity, and 4 months later, tense palmoplantar blisters appeared. Microscopic examination of the palmar blister revealed subepidermal vesicles characterized by eosinophil infiltration. Immunofluorescence analysis revealed linear IgG and C3 deposits along the basement membrane; ELISA testing confirmed the presence of anti‐BP180 NC16A IgG antibody, and MMP was diagnosed. The patient’s condition gradually improved with a therapeutic regimen of corticosteroids and immunoglobulins. A review of 10 cases of ICI‐associated MMP, including the present case, revealed clinical similarities to conventional MMP; in cases of persistent oral erosions due to ICI, it is most important to consider mucositis and MMP in the framework of differential diagnosis. Besides, we suggest that we can be more suspicious of MMP by paying attention to examining the palms and soles when the patient receiving ICIs has refractory oral ulcers. This report underscores the importance of careful observation and prompt management of irAE as cancer immunotherapy evolves.












 Open Access
Open Access