|
ISSN: 2573-5985 (online) Journal Abbreviation: Trends Immunother. |
Trends in Immunotherapy (TI) is an open access peer-reviewed journal encompassing various disciplines related to all immune-system-based areas. TI has a target audience consisting of scientific researchers, professional practitioners, and medical scholars from academia, the medical industry, education, etc. It provides a forum to share scholarly works to advance immunotherapy with the combination of science and medicine. TI publishes original research articles, review articles, editorials, mini-review articles, case reports, commentaries, correspondence articles, database articles, perspective articles, short reports, etc. Preliminary studies and pre-clinical and clinical investigative reports are welcome.
Important: The ownership of the journal Trends in Immunotherapy (eISSN: 2573-5985) will be transferred from EnPress Publisher LLC to UK Scientific Publishing Limited. Starting from Volume 9, Issue 1, 2025, UK Scientific Publishing Limited will take over the publication of this journal. Please note that from September 6, 2024, all new submissions should be made through the following link: https://ojs.ukscip.com/index.php/ti/submission/wizard. |
Vol 8, No 2: (Published)
Table of Contents
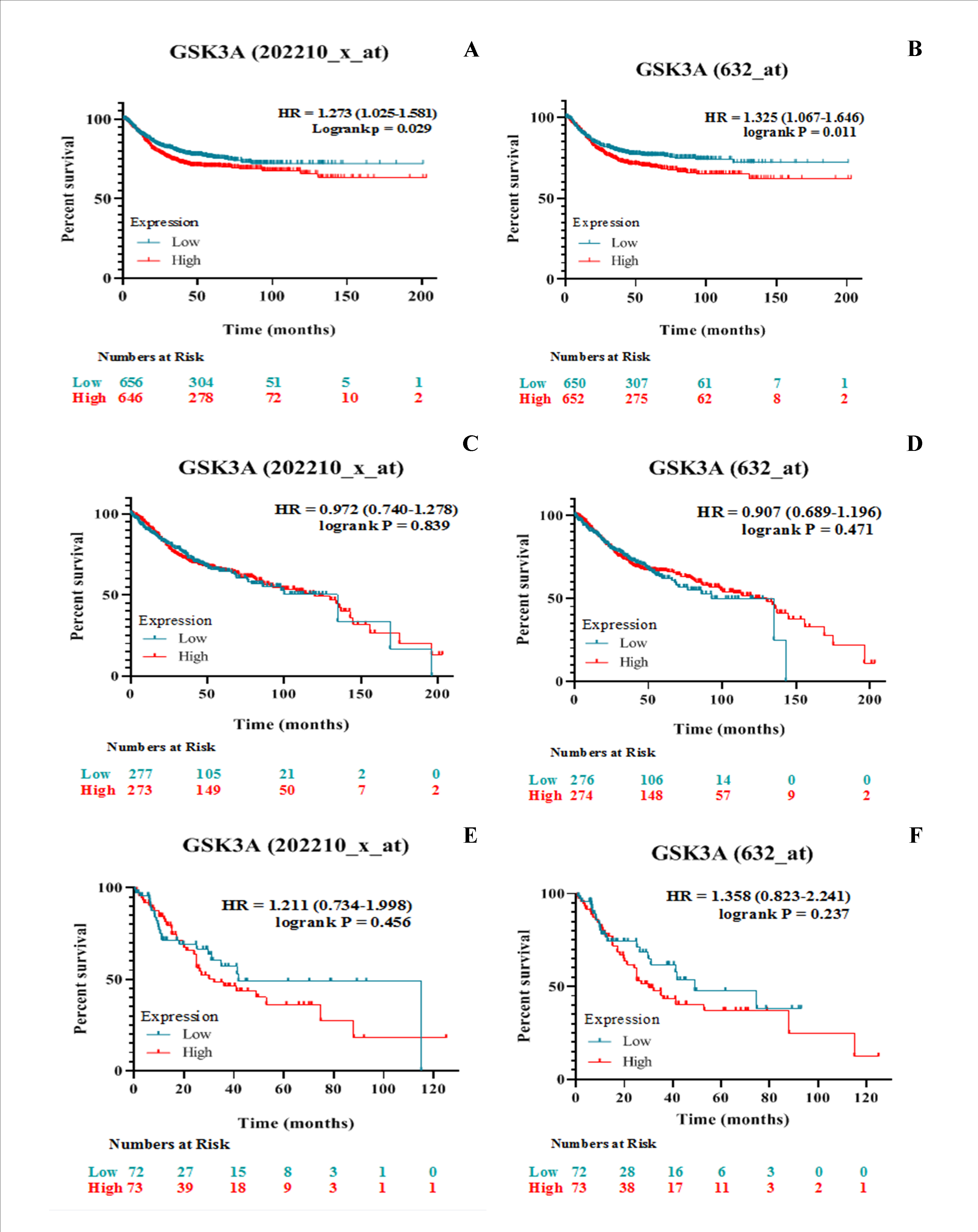
Introduction: GSK3, a multifunctional serine/threonine kinase regulates cell-cycle progression, differentiation and apoptosis and its inhibition can have a tumor suppressor/promoter effect, depending on the cell type. There are conflicting reports of GSK3 in cell growth, but most studies have focused on GSK3β and very few on GSK3α in cancer. GSK3α regulates proliferation of melanoma and pancreatic and colon cancer cells, but the predictive role of GSK3A is not known in colon cancer. Material and methods: The prognostic role of GSK3A was assessed in colon cancer patients employing Kaplan-Meier plotter (KM plotter) database. Online ROC plotter tool was used to compare the GSK3A gene expression in colorectal cancer patients receiving any form of chemotherapy. Results: Current results show that higher GSK3A mRNA expression is significantly related to poorer Relapse Free Survival (RFS) in colon cancer patients. Assessment of GSK3A mRNA for different clinicopathological features like clinical stages, TP53 mutation, stage T and stage N highlighted the critical prognostic value of GSK3A mRNA in colon cancer. Discussion and conclusion: GSK3A will help to better predict colon cancer prognosis and to develop better treatment strategies for colon cancer patients and will be beneficial in combating the heterogeneity and complexity of colon cancer.
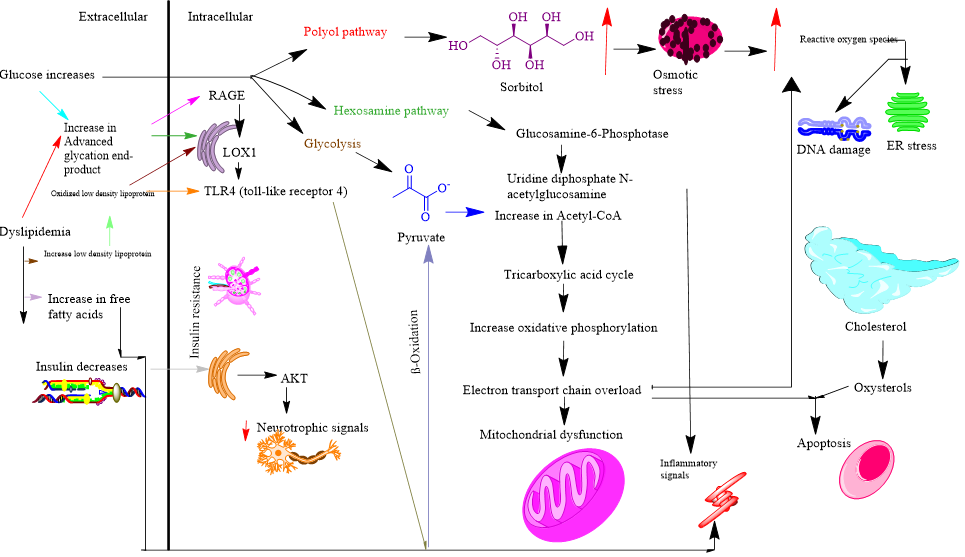
Diabetes mellitus is one of the main chronic metabolic syndromes that contains a number of repercussions and risk factors because hyperglycemia leads other organs to malfunction. Despite the existence of cutting-edge methods for the treatment of diabetes, the proper therapeutic medication distribution remains a serious worry in the current situation. Betaine, also known as N,N-trimethyl glycine, is an amino acid derivative with a number of advantageous health effects. This chemical is available to both humans and other animals because it is consumed and created endogenously. Additionally, some pathological conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, result in a decrease in the amount of betaine in the tissues. Betaine has been found in rodent studies to considerably lessen a number of abnormalities associated with diabetes. changes in the liver and other insulin-sensitive organs. Researchers believe that AMP-activated protein kinase is crucial to the mechanism through which betaine exerts its anti-diabetic effects. Also, betaine has been demonstrated to reduce endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in rodent models of diabetes. Since betaine has shown promising therapeutic benefits in animal trials, its potential use in treating diabetes has been raised.
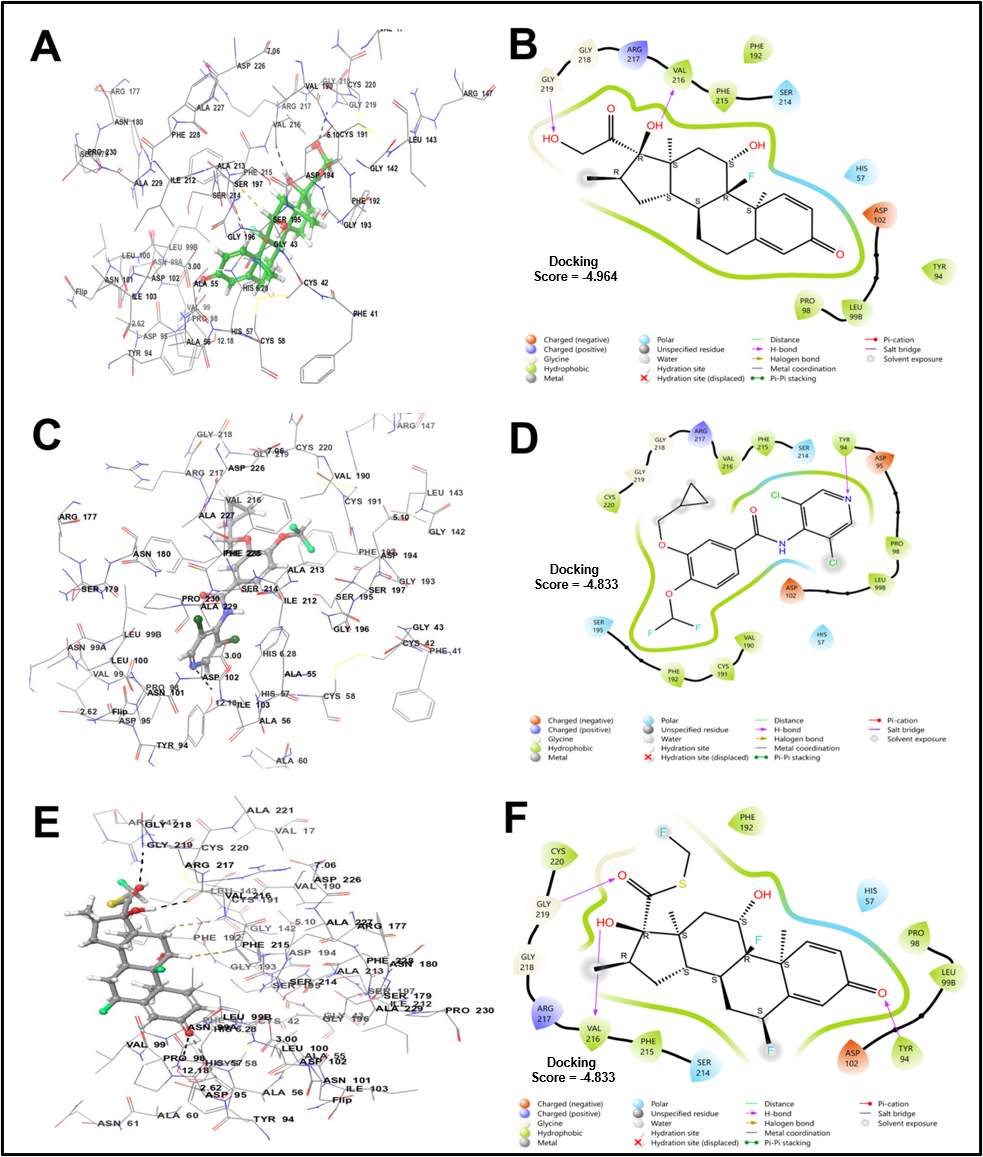
With increasing environmental pollution (rising levels of air borne allergens) and smoke inhalational habits, biomass smoke, etc. all affect lung health, leading to various chronic lung diseases, and among them, life-threatening chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is growing in prevalence around the globe. Thus, it’s a great demand from researchers to discover novel therapeutic drugs and vaccines against COPD. Human neutrophil elastase (HNE) is a major inflammatory protein that triggers inflammation in chronic airway diseases, causing airway remodeling and cytokines release. Recently, it has emerged as a significant target for drug discovery in patients with COPD. Hence, this study aimed to investigate the In-silico screening of the phytochemical medicinal plant Tridax procumbens against COPD via targeting HNE using the Schrodinger suite 2023-1. The docking score, glide score, and binding energy were calculated by the glide program using the Prime MM-GB/SA (Molecular Mechanics with Generalized Born and Surface Area Solvation) module. The best selected phytochemicals (ligands) were then screened for pharmacokinetic properties via ADMET analysis predicted using the qikProp program. Out of the library of Tridax procumbens, the phytochemicals like Apigetrin, Puerarin, Centaureidin, and Myricetin significantly bind to the catalytic site of HNE with PHE41, CYS42, SER195, GLY193, PHE192, HIS57, CYS58, PHE215, SER214, ASN61, LEU998, PRO98, TYR94, and ASP95 as residues with a glide score of the highest binding affinity (−7.707, −7.707, −7.045, and −6.871, respectively) compared to the standard drugs; Dexamethasone (−4.964), Roflumilast (−4.833), and Fluticasone (−3.968). The ADMET analysis of these four phytochemicals showed good pharmacokinetic profiles with human oral absorption, log S, molar volume, and van der waals volume, etc. Thus, In-silico findings suggest that carrying out these phytochemicals (Apigetrin, Puerarin, Centaureidin, and Myricetin) from Tridax procumbens to validate their therapeutic potential against COPD at preclinical and clinical levels.
The statement “prevention is better than cure” and its applications is not a new for Ayurvedic health care system. The statement defines the aim and objectives of Ayurvedic health care system in a nutshell “swasthasya swasthya rakshanam aaturasya vikara prashamanam”. The immune system is certainly considered one of our most discreet biological systems withinside the body. Immunizations may be obtained by us actively or passively. Active immunization includes stimulating with an antigen to generate immunological defenses against a destiny exposure, rather than passive vaccination, which includes administering antibodies to someone who has already been exposed to an antigen. Both plant and animal sources produce immunomodulatory effects to boost the body’s immunological reactivity against infections by engaging the non-specific immune system. Herbal immunomodulators are substances that either activate or suppress innate and adaptive immune responses in the body. Different ailments including allergies, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, and other infectious disorders are caused by immune system failure. Therefore, regulating the many infectious illnesses requires significant immune response modification. Global scientific study is currently focused on how various medicinal plant components might alter the immune system. Numerous Indian and “Rasayana” and medicinal plants may have immunomodulatory characteristics. Some of these plants are Tinospora cordifolia, Morus alba, Acacia catechu, Allium sativum, and Mangifera indica. There are many more that are still undiscovered and offer space for greater study.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is characterized by hyperglycemia, which is a common endocrine disease. DM and its complications may lead to diabetic foot ulcers (DFU). DFU is associated with reduced wound healing because of altered cellular and cytokine responses, inadequate vascularization, infection, and neuropathy. One novel and promising approach to treating diabetic wound healing is the administration of compounds based on nanotherapeutics, such as nanoparticles and nanoscaffolds. Plant extracts can be administered more successfully by using nanoscale delivery methods. Plant extracts and their related phytocompounds can be nanostructured to enhance their bioavailability, regulate their release via extended delivery techniques to the wound site, and increase their penetration to the deeper layers of the skin. All these benefits are critical for the healing process. This brief overview covers the most recent methods to develop phytomedicine nanotherapeutics for the treatment of diabetic wounds.
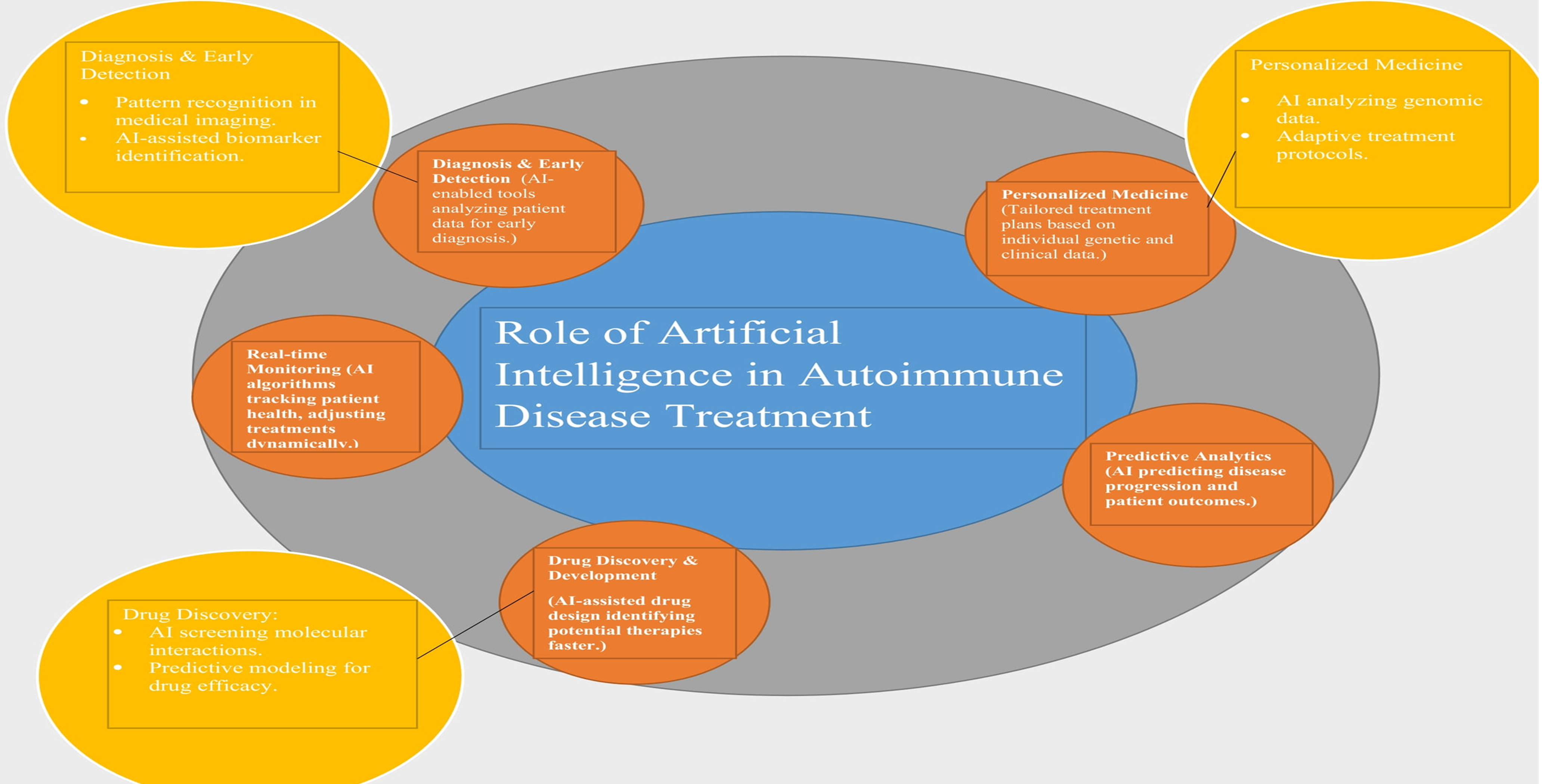
The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) into medical practice has considerably improved the treatment of autoimmune disorders, opening new avenues for personalized therapy. This study examines advances in AI-driven therapeutic options for autoimmune illnesses, including both current and developing treatments. Traditional therapies for autoimmune illnesses, such as immunosuppressive therapy and biologics, attempt to alleviate symptoms but frequently fall short of offering personalized care. Emerging approaches, such as precision medicine and artificial intelligence, are altering the landscape by harnessing massive volumes of patient data to better customize therapies. AI holds the ability to transform autoimmune disease therapy by enhancing diagnosis, discovering biomarkers, optimizing drug development, and personalized treatment procedures. Real-world applications and case studies are examined to demonstrate how machine learning algorithms have improved treatment tactics for rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and multiple sclerosis. While AI has many advantages, like enhanced diagnosis accuracy and personalized therapy, it also has drawbacks, such as data privacy, the requirement for vast datasets, algorithmic bias, and a lack of explain ability. This study emphasizes the advantages of AI, such as improved patient stratification and predictive modelling, while also discussing its drawbacks, such as ethical problems and the possibility of data exploitation. AI presents intriguing prospects for treating autoimmune diseases, but more research and cooperation are required to overcome current difficulties and completely integrate AI into clinical practice.
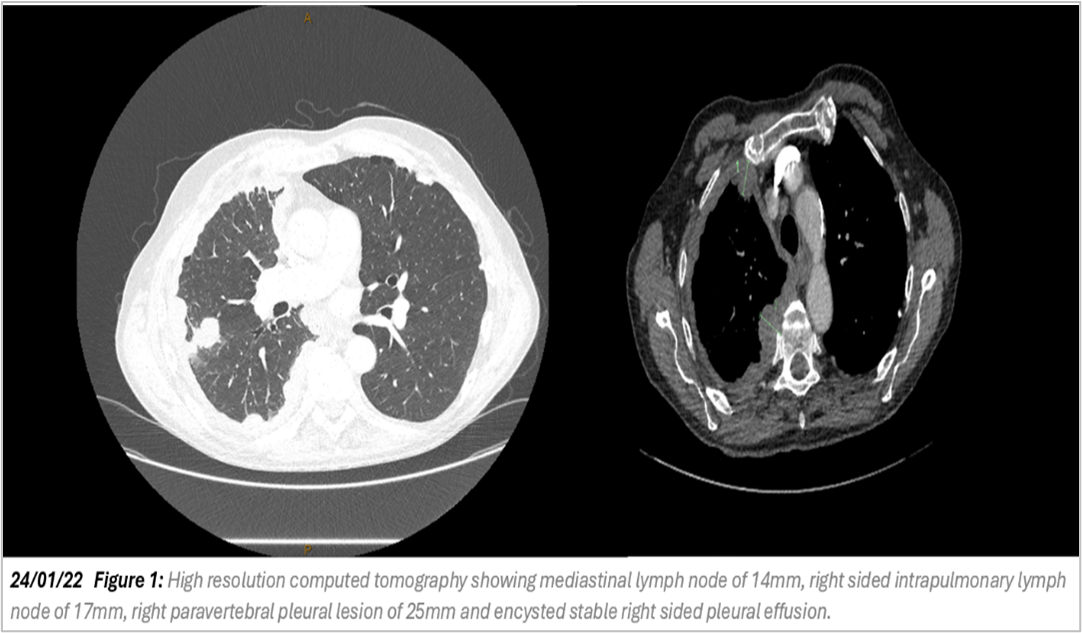
Malignant pleural mesothelioma has a poor prognosis with limited therapeutic options Although numerous trials have shown that combination immunotherapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab is one of the first line treatments for patients with unresectable MPM, there is limited data on delayed responses over a long follow up period. We report a case of a delayed response 7 months after the cessation of immunotherapy in a patient who initially had progressive malignant pleural mesothelioma with metastases.
New hope for patients with specific blood malignancies has arisen with the emergence of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy as a revolutionary approach to cancer immunotherapy. This groundbreaking therapy modifies a patient’s immune system such that their own T cells can identify and destroy cancer-specific antigens by expressing CARs. Multiple myeloma, lymphomas, and leukemias are among the blood malignancies that have been treated with six CAR T-cell treatments that have been approved by the FDA since 2017. The treatment entails drawing T cells out of the patient’s blood, changing their genes to produce CARs, and then reintroducing these modified cells into the patient. The CAR T-cells have the ability to identify cancer cells, proliferate, and kill them once they enter the circulation. This might lead to long-term protection from the illness. Patients with blood malignancies who have relapsed or are resistant to previous treatments have shown encouraging results in clinical studies, with some patients even managing to achieve long-term remissions. Cytokine release syndrome and neurological toxicities are two of the many potential adverse effects of CAR T-cell treatment that must be carefully managed. The complicated production method and expensive treatment cost further restrict its broad availability. Research is ongoing with the goals of improving the safety profile, increasing the effectiveness, and expanding the applicability of CAR T-cell therapy to solid tumors.
Announcements
Publisher Changed |
|
The ownership of the journal Trends in Immunotherapy (eISSN: 2573-5985) will be transferred from EnPress Publisher LLC to UK Scientific Publishing Limited. Starting from Volume 9, Issue 1, 2025, UK Scientific Publishing Limited will take over the publication of this journal. Please note that from September 6, 2024, all new submissions should be made through the following link: https://ojs.ukscip.com/index.php/ti/submission/wizard. |
|
| Posted: 2024-09-06 | |
| More Announcements... |












 Open Access
Open Access