Research News: Harnessing artificial intelligence (AI) towards the landscape of big earth data: Methods, challenges, opportunities, future directions |
|
Highlights:
|
|
| Posted: 2025-06-04 | More... |
Notification of publication frequency change! |
|
.jpg) |
|
| Posted: 2025-01-10 | More... |
Congratulations to our Editorial Board Member Prof. Danfeng Hong, on Being Recognized as a 2024 Highly Cited Award Recipient by Clarivate Analytics |
|
 |
|
| Posted: 2024-12-09 | More... |
Welcome to the two Co-Editors-in-Chief! |
|
We are pleased to announce that Prof. Yanfang Sang and Prof. Jorge Olcina-Cantos have been appointed as Co-Editors-in-Chief of this journal.  |
|
| Posted: 2024-02-24 | More... |
JGC will been indexed by GeoRef database! |
|
 |
|
| Posted: 2024-02-19 | More... |
New Author Guidelines are updated! |
|
| Before submitting to our online submission system, please carefully check that your manuscript has been prepared in accordance with the step-by-step instructions. The guide and the EnPress Manuscript Submission Template are updated and prepared specifically for those who are going to contribute or edit the manuscripts to be published in Journal of Geography and Cartography since 2024 Volume 7 Issue 1. | |
| Posted: 2023-12-20 | |
Research News: Spatial analysis and mapping of malaria risk areas using multi- criteria decision making in Ibadan, Oyo state, Nigeria |
|
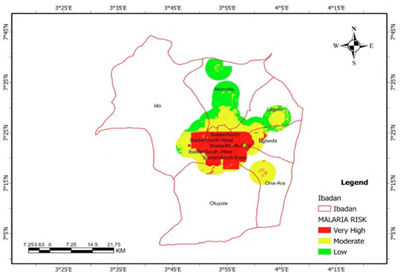 Figure 1. Final malaria risk map. |
|
| Posted: 2023-10-24 | More... |
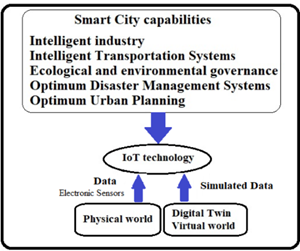
Research News: Digital twins and 3D information modeling in a smart city for traffic controlling: A review |
|
Figure1. The diagram of the relationship between the digital |
|
| Posted: 2023-07-08 | More... |
Notification of frequency of publication |
|
| Journal of Geography and Cartography (eISSN: 2578-1979, J. Geogr. Cartogr.) publishes 2 issues per year (every June, December since 2023). | |
| Posted: 2022-12-30 | |
Meet one of the outstanding editors! |
|
Dr. Mohammad H. Vahidnia Islamic Azad University Iran, Islamic Republic of |
|
| Posted: 2022-09-18 | More... |
Call for papers |
|
|
|
| Posted: 2022-02-10 | More... |
Research News: How to find and evaluate the groundwater ? |
|
Long-term drought and improper maintenance of water resources have intensified the contradiction between the supply and demand of water resources. Groundwater is developed and utilized by more and more regions because of its excellent water quality and stable water quantity. Human beings have an increasing demand for groundwater. Therefore, how to evaluate groundwater resources is an urgent problem to be solved.
|
|
| Posted: 2021-09-03 | More... |
Research News: The possible reasons of the coastline changing |
|
The coast divides into three types: coast, lake bank, and riverbank. It is a waterfront zone formed by the action of waves, tides, and currents at the contact between water surface and land. The bank formed by the accumulation of many sediments is called the beach. The coastline is the boundary between land and sea. The demarcation of the coastline is defined by the elevation of the submerged surface of the normal high tide level, that is, the submerged surface is the sea area and the dry-out zone is the land area.
|
|
| Posted: 2021-08-26 | More... |
Research News: Global 10-meter mangrove distribution data product release |
|
On August 12th, the State Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Information System, Institute of Geographical Sciences and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences released the 10-meter resolution data product of global mangrove distribution, which is the highest resolution and latest product in global mangrove data at present. The product is produced by Su Fenzhen's team, which aims to provide basic data support for the research of carbon neutrality, global change and sustainable development by using the intelligent remote sensing extraction method of big data. |
|
| Posted: 2021-08-21 | More... |
Research News: Impact of emission from a coal-fired power plant on air quality |
|
Coal combustion has been increasing rapidly in much of Asia, including in China and India (IPCC, 2013). Fine particulate matter (PM2.5: particles with an aerodynamic diameter of ≤2.5 μm) emitted/formed from coal combustion are key outdoor air pollutants of great environmental concern because they have serious adverse effects on public health (IARC, 2013).
|
|
| Posted: 2021-04-18 | More... |
Research News: How can reduce the response of building structures to seismic excitations |
|
Reinforced concrete (RC) is the most commonly used construction material used these days, primarily owning to its low cost, easy availability of materials, simpler execution without requirements of any special machineries or labour. Generally, the RC buildings are analyzed and designed such that, the moment resisting frame actions are developed in each member. The masonry infill wall are normally considered as non-structural elements used to create partitions or to protect the inside of the building and thus are ignored while analysis and design. However, under the action of lateral forces like the once due to earthquake and wind, these infill wall panel’s stiffness, strength and mass affect the behavior of RC frame building.Earthquakes are thus a severe structural hazard for structures designed for gravity loads as they may not sustain the horizontal shaking. Structures like buildings, elevated surface reservoir, bridges, towers, etc. may experience extreme vibrations during earthquake.
|
|
| Posted: 2021-03-30 | More... |
Research News: How can reduce the risk of wildfires |
|
Wildfires are a phenomenon that can alter ecosystems, damage property and infrastructure, and harm the wellbeing of at-risk populations. This trend in larger, more severe wildfires escalates the need for improved wildfire prevention planning by land managers. Improved planning requires fire risk mapping to identify the most at risk areas. Fire risk mapping has been an ongoing area of research for decades but no agreed upon method has yet been developed. Typically, fire risk mapping applies remote sensing and existing geographic data to acquire variables entered into a spatially explicit model to determine the hazard for specific areas and then evaluate the risk on the consequences of these hazards. This enables the land managers to address areas of high fire risk and reduce the current risk to better prepare for future fire events.
|
|
| Posted: 2021-03-12 | More... |
Notice on adjusting the frequency of publication |
|
Dear authors: Thanks to the efforts of editorial board members and editors, JGC has been supported and encouraged by more scholars. Thank you for your recognition and helpful suggestions. I would like to inform you that the publication frequency of JGC in 2021 has been changed to Semi-annual!
JGC editorial office |
|
| Posted: 2020-11-20 | More... |
Research News: Television and geography as big data: mapping a decade of television News |
|
Geography is closely related to human life, and the application of geography technology can bring a new perspective for human to see the world.
|
|
| Posted: 2020-08-20 | More... |
Research News: To detect the influence of natural factors on the spatial distribution of regional population by geographic detectors |
|
With the intensification of global climate change and resource and environmental problems, the relationship between people and geography has turned to re-examining the relationship between population, resources, environment and sustainable development. Based on spatial statistical analysis, facing new problems and new challenges, starting to learn from Quantitative research methods and techniques such as economics, behavioral science, systems science, and spatial information technology.
|
|
| Posted: 2020-06-15 | More... |
Call for papers for Special Issue of 2020 |
|
Call for papers for Special Issue of 2020: Man-land Research by analyzing and mapping geographic phenomena using cartographic methods in China. |
|
| Posted: 2019-11-20 | More... |
Call for papers |
|
Dear scholars/researchers, The Journal of Geography and Cartography invites article submissions for the publication of Vol.2 Issue 1 in 2019. Journal of Geography and Cartography (JGC) is an international open-access academic journal with rigorous peer-reviewed process. Its scope covers geography science, geochemistry, natural geography, geophysics, environment science, geographic information system, and all fields of geography and cartography. Our ultimate goal is to make the journal a platform of global academic sources for high-quality geo-papers. Topics in cartography, remote sensing technique and man-land relationship by analyzing and mapping geographic phenomena using cartographic methods, and more are welcomed. JGC publishes original research articles, review articles, editorials, reports, brief commentaries, perspectives, etc. |
|
| Posted: 2018-11-20 | More... |
Research News: See beauty through the eyes of a master cartographer |
|
If you were to drop Dave Imus anywhere in the United States, he could likely point out something unique in the landscape around him. This winding road through flat farmland, 30 miles outside of Eugene, Oregon, is no different. “This spot has the unique characteristic in that you can see all five of Oregon’s highest snow peaks in the Cascade Range,” Imus said pointing to the mountain range obscured by clouds and distance. “One thing I’ve learned is that all landforms, regardless of how subtle they are, have their own beauty and character.” |
|
| Posted: 2018-09-12 | |
Research News: Finding Nemo's genes |
|
An international team of researchers has mapped Nemo's genome, providing the research community with an invaluable resource to decode the response of fish to environmental changes, including climate change. In a breakthrough study led by the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) and the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies (Coral CoE), researchers used high-tech sequencing tools to create one of the most complete genetic maps for the orange clownfish, a common reef inhabitant and star of the Disney movie, Finding Nemo.  Clownfish (stock image). Credit: © cbpix / Fotolia |
|
| Posted: 2018-09-12 | |
Research News: Warming: Peatlands will store more carbon initially, but that will change |
|
Peatlands are extremely effective at storing carbon, but an international study featuring a University of Queensland researcher has found climate change could stop that. The group investigated how peatlands -- swamps and bogs with organic rich soils -- have responded to climate variability between 850 BCE and 1850 CE.  These are the peatlands of Moon Point on Queensland's Fraser Island. Credit: Patrick Moss |
|
| Posted: 2018-09-12 | More... |
| 1 - 25 of 25 Items | |






2.png)