With the intensification of global climate change and resource and environmental problems, the relationship between people and geography has turned to re-examining the relationship between population, resources, environment and sustainable development. Based on spatial statistical analysis, facing new problems and new challenges, starting to learn from Quantitative research methods and techniques such as economics, behavioral science, systems science, and spatial information technology.
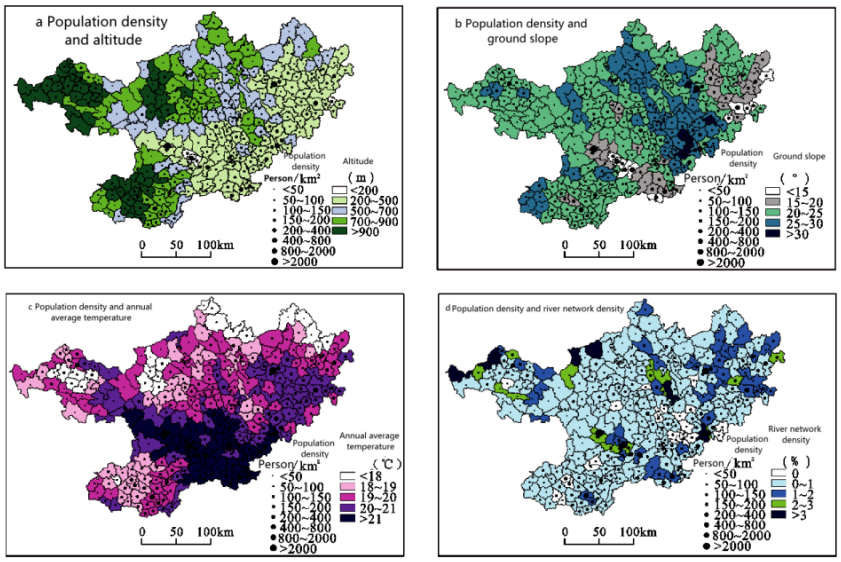
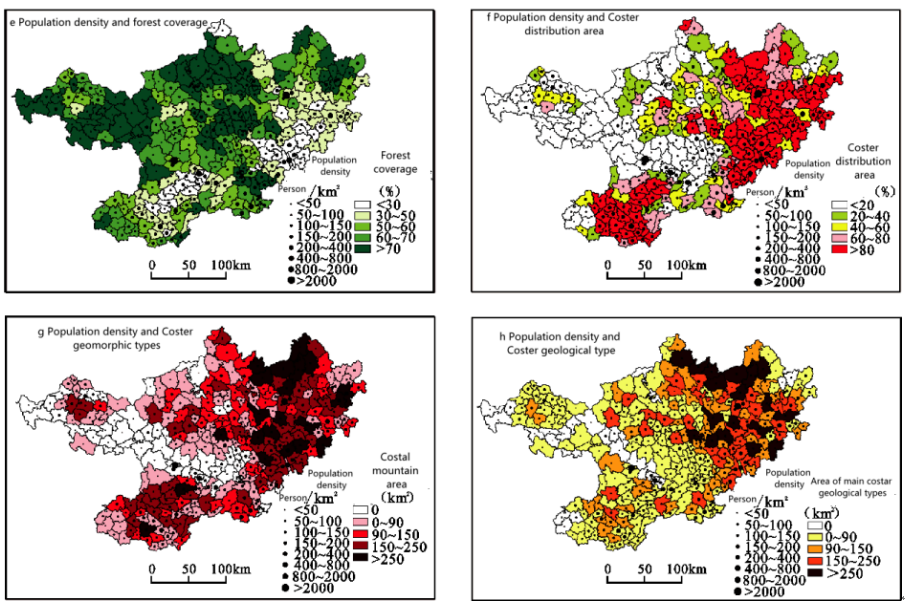
Shi Shana et al published the paper of “Population distribution characteristics and its relationship with natural factors in karst mountainous areas of Northwest Guangxi”, from which the factor detection results of the geographic detector show that the altitude has the greatest influence on the spatial distribution of the population( see Figure 1).
Figure 1. Spatial distribution of natural factors and population density in the northwestern Guangxi in 2010.
In the future, geographers will still pay attention to regional differences, vulnerabilities and spatial analysis, strengthen the study of spatialization methods of demographic data, and respond to new challenges in the relationship between people and geography from different geographic scales and dimensions.
Source from: [1] Feng Zhiming, Li Peng. Review of Population Geography in the Past Century.Progress in Geography 2011; 30(2):131-140. [2] Shi Shana, Xie Binggeng, Hu Baoqing, et al. Population distribution characteristics and its relationship with natural factors in karst mountainous areas of Northwest Guangxi. Journal of Geography and Cartography 2020; 3(1): 16-29. |