Full Issue
| View or download the full issue |
Table of Contents
We develop a relatively cheap technology of processing a scrap in the form of already used tungsten-containing products (spirals, plates, wires, rods, etc.), as well not conditional tungsten powders. The main stages of the proposed W-scrap recycling method are its dispersing and subsequent dissolution under controlled conditions in hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution resulting in the PTA (PeroxpolyTungstic Acid) formation. The filtered solution, as well as the solid acid obtained by its evaporation, are used to synthesize various tungsten compounds and composites. Good solubility of PTA in water and some other solvents allows preparing homogeneous liquid charges, heat treatment of which yield WC and WC–Co in form of ultradispersed powders. GO (Graphene Oxide) and PTA composite is obtained and its phase transition in vacuum and reducing atmosphere (H2) is studied. By vacuum-thermal exfoliation of GO–PTA composite at 170–500℃ the rGO (reduced GO) and WO2.9 tungsten oxide are obtained, and at 700℃—rGO–WO2 composite. WC, W2C and WC–Co are obtained from PTA at high temperature (900–1000℃). By reducing PTA in a hydrogen atmosphere, metallic tungsten powder is obtained, which was used to obtain sandwich composites with boron carbide B4C, W/B4C, and W/(B4C–W), as neutron shield materials. Composites of sandwich morphology are formed by SPS (Spark-Plasma Sintering) method.
Protein- and peptide-based medications are recognized for their effectiveness and lower toxicity compared to chemical-based drugs, making them promising therapeutic agents. However, their application has been limited by numerous delivery challenges. Polymeric nanostructures have emerged as effective tools for protein delivery due to their versatility and customizability. Polymers’ inherent adaptability makes them ideal for meeting the specific demands of protein-delivery systems. Various strategies have been employed, such as enzyme inhibitors, absorption enhancers, mucoadhesive polymers, and chemical modifications of proteins or peptides. This study explores the hurdles associated with protein and peptide transport, the use of polymeric nanocarriers (both natural and synthetic) to overcome these challenges, and the techniques for fabricating and characterizing nanoparticles.
Hospital waste containing antibiotics is toxic to the ecosystem. Ciprofloxacin is one of the essential, widely used antibiotics and is often detected in water bodies and soil. It is vital to treat these medical wastes, which urge new research towards waste management practices in hospital environments themselves. Ultimately minimizes its impact in the ecosystem and prevents the spread of antibiotic resistance. The present study highlights the decomposition of ciprofloxacin using nano-catalytic ZnO materials by reactive oxygen species (ROS) process. The most effective process to treat the residual antibiotics by the photocatalytic degradation mechanism is explored in this paper. The traditional co-precipitation method was used to prepare zinc oxide nanomaterials. The characterization methods, X-Ray diffraction analysis (XRD), Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Ulraviolet-Visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), Scanning Electron microscopy (SEM) and X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) have done to improve the photocatalytic activity of ZnO materials. The mitigation of ciprofloxacin catalyzed by ZnO nano-photocatalyst was described by pseudo-first-order kinetics and chemical oxygen demand (COD) analysis. In addition, ZnO materials help to prevent bacterial species, S. aureus and E. coli, growth in the environment. This work provides some new insights towards ciprofloxacin degradation in efficient ways.
Every production day in Nigeria, and in other oil producing countries, millions of barrels of produced water is generated. Being very toxic, remediation of the produced water before discharge into environment or re-use is very essential. An eco-friendly and cost effective approach is hereby reported for remediative pre-treatment of produced water (PW) obtained from Nigerian oilfield. In this approach, Telfairia occidentalis stem extract-silver nanoparticles (TOSE-AgNPs) were synthesized, characterized and applied as bio-based adsorbent for treating the PW in situ. The nanoparticles were of average size 42.8 nm ± 5.3 nm, spherical to round shaped and mainly composed of nitrogen and oxygen as major atoms on the surface. Owing to the effect of addition of TOSE-AgNPs, the initially high levels (mg/L) of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and TSS of 607, 3.78 and 48.4 in the PW were reduced to 381, 1.22 and 19.6, respectively, whereas DO and COD improved from 161 and 48.4 to 276 and 19.6 respectively, most of which fell within WHO and US-EPA safe limits. Particularly, the added TOSE-AgNPs efficiently removed Pb (II) ions from the PW at temperatures between 25 ℃ to 50 ℃. Removal of TOSE-AgNPs occurred through the adsorption mechanism and was dependent contact time, temperature and dose of TOSE-AgNPs added. Optimal remediation was achieved with 0.5 g/L TOSE-AgNPs at 30 ℃ after 5 h contact time. Adsorption of Pb (Ⅱ) ions on TOSE-AgNPs was spontaneous and physical in nature with remediation efficiency of over 82% of the Pb (Ⅱ) ions in solution. Instead of discarding the stem of Telfairia occidentalis, it can be extracted and prepared into a new material and applied in the oilfield as reported here for the first time.
Nickel Oxide (NiO) nanoparticles (NPs), doped with manganese (Mn) and cobalt (Co) at concentrations up to 8%, were synthesized using the composite hydroxide method (CHM). X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis confirmed the formation of a cubic NiO structure, with no additional peaks detected, indicating successful doping. The average crystallite size was determined to range from 15 to 17.8 nm, depending on the dopant concentration. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images revealed mostly spherical, agglomerated particles, likely due to magnetic interactions. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) confirmed the incorporation of Mn and Co into the NiO lattice, consistent with the XRD results. The dielectric properties exhibited a high dielectric constant at low frequencies, which can be attributed to ion jump orientation and space charge effects. The imaginary part of the dielectric constant decreased with increasing frequency, as it became harder for electrons to align with the alternating field at higher frequencies. Both the real and imaginary dielectric constants showed behavior consistent with Koop’s theory, increasing at low frequencies and decreasing at higher frequencies. Dielectric loss was primarily attributed to dipole flipping and charge migration. AC conductivity increased with frequency, and exhibited higher conductivity at high frequencies due to small polaron hopping. These co-doped NPs show potential for applications in solid oxide fuel cells.
Zinc oxide (ZnO) hollow spheres are gaining attention due to their exceptional properties and potential applications in various fields. This study investigates the impact of different zinc precursors Zinc Chloride (ZnCl2), Zinc Nitrate [Zn(NO3)2], and Zinc Acetate [Zn(CH3COO)2] on the hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO hollow spheres. A comprehensive set of characterization techniques, including Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) analysis, was utilized to assess the structural and morphological features of the synthesized materials. Our findings demonstrate that all samples exhibit a high degree of crystallinity with a wurtzite structure, and crystallite sizes range between 34 to 91 nm. Among the different precursors, ZnO derived from Zinc Nitrate showed markedly higher porosity and a well-defined mesoporous structure than those obtained from Zinc Acetate and Zinc Chloride. This research underscores the significance of precursor selection in optimizing the properties of ZnO hollow spheres, ultimately contributing to advancements in the design and application of ZnO-based nanomaterials.
Cysteine is one of the body’s essential amino acids to build proteins. For the early diagnosis of a number of diseases and biological issues, L-cysteine (L-Cys) is essential. Our study presents an electrochemical sensor that detects L-cysteine by immobilizing the horseradish peroxidase (HRP) enzyme on a reduced graphene oxide (GCE) modified glassy carbon electrode. The morphologies and chemical compositions of synthesized materials were examined using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). The modified electrode’s electrochemical behavior was investigated using cyclic voltammetry (CV). Cyclic voltammetry demonstrated HRP/rGO/GCE has better electrocatalytic activity than bare GCE in the oxidation of L-cysteine oxidation in a solution of acetate buffer. The electrochemical sensor had a broad linear range of 0 µM to 1 mM, a 0.32 µM detection limit, and a sensitivity of 6.08 μA μM−1 cm−2. The developed sensor was successfully used for the L-cysteine detection in a real blood sample with good results.
This review focuses on ferrites, which are gaining popularity with their unique properties like high electrical resistivity, thermal stability, and chemical stability, making them suitable for versatile applications both in industry and in biomedicine. This review is highly indicative of the importance of synthesis technique in order to control ferrite properties and, consequently, their specific applications. While synthesizing the materials with consideration of certain properties that help in certain methods of preparation using polyol route, green synthesis, sol-gel combustion, or other wise to tailor make certain properties shown by ferrites, this study also covers biomedical applications of ferrites, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), drug delivery systems, cancer hyperthermia therapy, and antimicrobial agents. This was able to inhibit the growth of all tested Gram-negative and positive bacteria as compared with pure ferrite nanoparticles without Co, Mn or Zn doping. In addition, ferrites possess the ability to be used in environmental remediation; such as treatment of wastewater which makes them useful for high-surface-area and adsorption capacity due heavy metals and organic pollutants. A critical analysis of functionalization strategies and possible applications are presented in this work to emphasize the capability of nanoferrites as an aid for the advancement both biomedical technology and environmental sustainability due to their versatile properties combined with a simple, cost effective synthetic methodology.
This review provides an overview of the importance of nanoparticles in various fields of science, their classification, synthesis, reinforcements, and applications in numerous areas of interest. Normally nanoparticles are particles having a size of 100 nm or less that would be included in the larger category of nanoparticles. Generally, these materials are either 0-D, 1-D, 2-D, or 3-D. They are classified into groups based on their composition like being organic and inorganic, shapes, and sizes. These nanomaterials are synthesized with the help of top-down bottom and bottom-up methods. In case of plant-based synthesis i.e., the synthesis using plant extracts is non-toxic, making plants the best choice for producing nanoparticles. Several physicochemical characterization techniques are available such as ultraviolet spectrophotometry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, the atomic force microscopy, the scanning electron microscopy, the vibrating specimen magnetometer, the superconducting complex optical device, the energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to investigate the nanomaterials. In the meanwhile, there are some challenges associated with the use of nanoparticles, which need to be addressed for the sustainable environment.
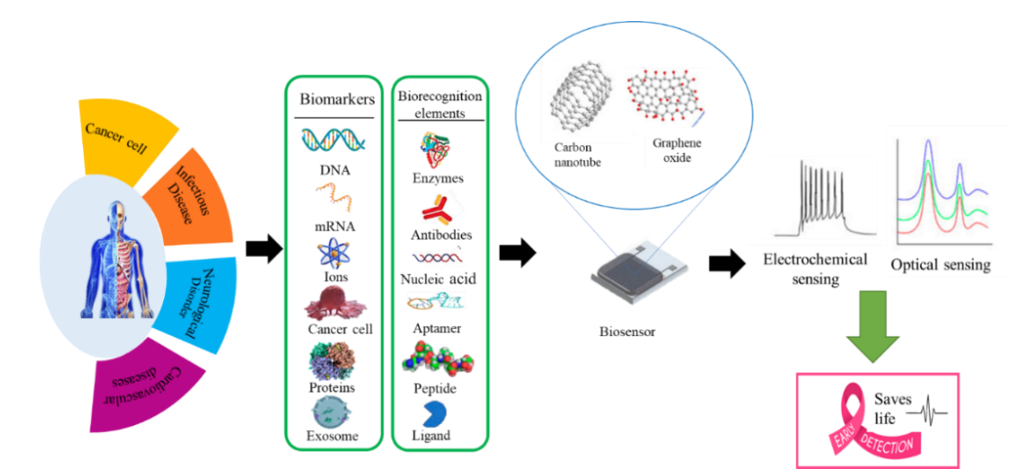
This review discusses the significant progress made in the development of CNT/GO-based biosensors for disease biomarker detection. It highlights the specific applications of CNT/GO-based biosensors in the detection of various disease biomarkers, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, infectious diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders. The superior performance of these biosensors, such as their high sensitivity, low detection limits, and real-time monitoring capabilities, makes them highly promising for early disease diagnosis. Moreover, the challenges and future directions in the field of CNT/GO-based biosensors are discussed, focusing on the need for standardization, scalability, and commercialization of these biosensing platforms. In conclusion, CNT/GO-based biosensors have demonstrated immense potential in the field of disease biomarker detection, offering a promising approach towards early diagnosis. Continued research and development in this area hold great promise for advancing personalized medicine and improving patient outcomes.


_1.jpg)
 Open Access
Open Access