Full Issue
| View or download the full issue |
Table of Contents
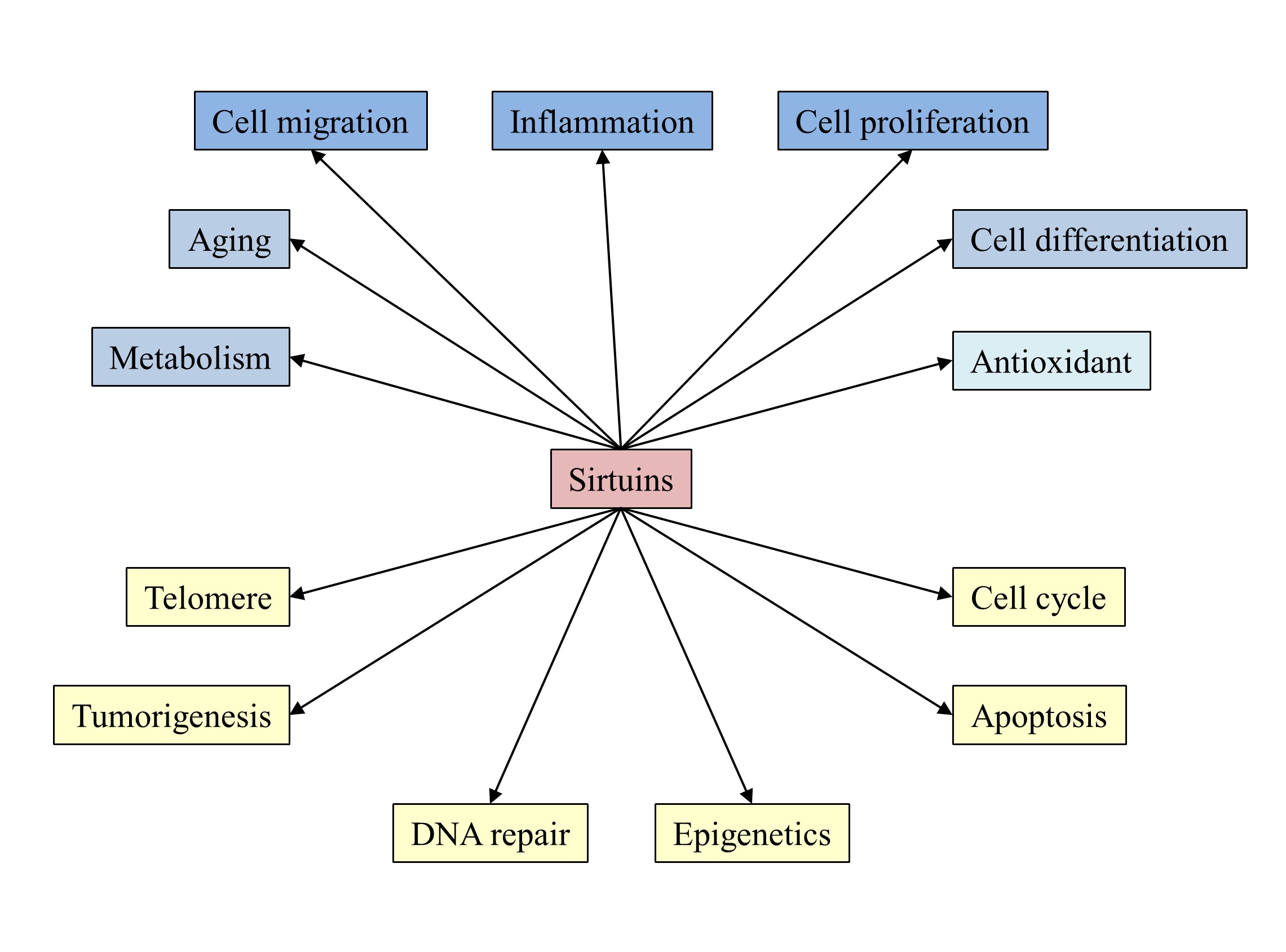
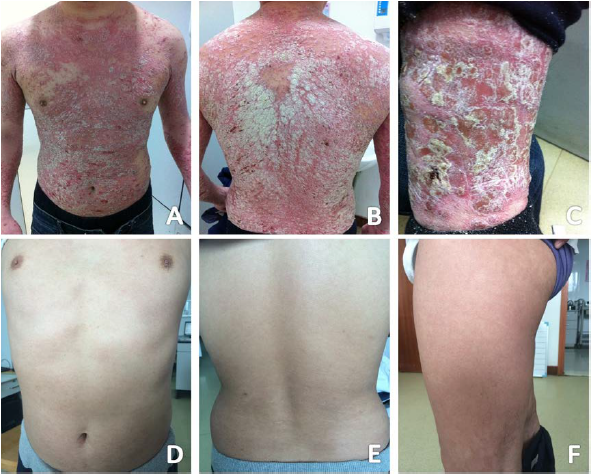
Sirtuins (SIRTs) are initially recognized as NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase. SIRTs attract attention for their role as calorie restriction-induced “longevity proteins” to be expected to extend human life span and to promote health. As advancing studies, SIRTs have been recognized as cell signaling regulators which contribute to anti-inflammation, cell differentiation and so on. Therefore, SIRTs are supposed to affect wound healing which is comprised highly orchestrated complex four phases: hemostasis, inflammation, tissue formation and tissue remodeling. This review highlights the roles of SIRTs in wound healing process and provides a foundation and impetus for future basic and clinical research.












 Open Access
Open Access