Guidelines on Self-Citation Rates for Submissions |
|
The editorial office appreciates the interest and support for Sustainable Forestry. As authors prepare to submit their manuscripts, they are advised to pay attention to the following guidelines regarding self-citation rates: |
|
| Posted: 2024-11-04 | More... |
The new standard will contribute to the promotion of responsible forest management and becomes effective on 15 March 2025. |
|
After a long period of participative construction with members, public consultations and field tests, the new national standard for forest plantations will replace the current Brazilian standards that include plantations in the scope (the Harmonized Certification Bodies’ standard and standard for SLIMF). |
|
| Posted: 2024-09-12 | More... |
Release of the State of the World’s Forests 2024 Report |
|
@securesustain.org |
|
| Posted: 2024-07-23 | More... |
Notice on Preprint Policy |
|
Sustainable Forestry recognizes the benefits of preprints to authors and the research community. Therefore, the journal accepts submissions that are shared via preprint platforms, with the understanding that these submissions have not undergone peer review. |
|
| Posted: 2024-06-01 | More... |
Editorial Board Recruitment for Sustainable Forestry |
|
|
|
| Posted: 2024-04-12 | More... |
Please follow the new Author Guidelines for your submission! |
|
| Please follow the journal's author guideline and the required article template to prepare your manuscript. | |
| Posted: 2024-01-26 | More... |
New version of author guideline format |
|
Please follow the journal's author guideline and the required article template to prepare your manuscript. |
|
| Posted: 2023-09-06 | More... |
SF has been included in the CAS databases! |
|
We are glad to announce that Sustainable Forestry (SF) has been included in the CAS databases! The response email is as follows: I am pleased to inform you that Sustainable Forestry [ISSN: 2578-2002], has been found suitable for inclusion in the CAS databases. We will begin coverage with volume 5, issue 1. We will routinely check the website and put the new issue into ourproduction system. If you have questions or concerns, please don’t hesitate to contact me. Best regards, Thanks to all the authors and reviewers!
|
|
| Posted: 2023-04-14 | More... |
The “Conflict of Interest” policy |
|
For the sake of academic fairness, all authors are required to declare all activities that have the potential to be deemed as a source of competing interest in relations to their submitted manuscript. Examples of such activities could include personal or work-related relationships, events, etc. Authors who have nothing to declare are encouraged to add "The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest" in this section. A declaration of interests for all authors should be received before an article can be reviewed and accepted for the publication. As the authors, editors or reviewers, they also are required to declare the conflict of interest in academy.
Editorial Office |
|
| Posted: 2022-08-01 | More... |
International Day of Forests |
|
 @WorldAtlas |
|
| Posted: 2022-03-23 | More... |
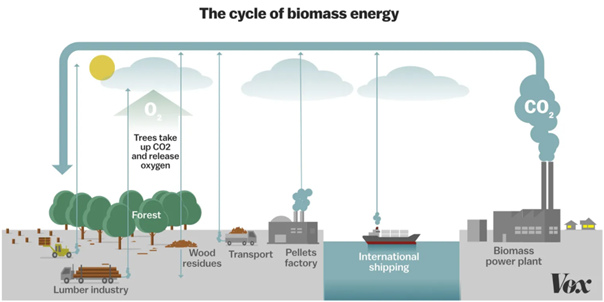
Biomass energy production & carbon neutral |
|
@Vox |
|
| Posted: 2022-03-06 | More... |
Congratulations to our one of the outstanding editors to be on the list of World’s Most Influential Scientists (2021)! |
|
Faculty of Engineering and Architecture Department of Landscape Architecture, Kastamonu University Turkey |
|
| Posted: 2021-12-12 | More... |
Education is a key lifeline for world’s forests |
|
New survey points out that forest education must be strengthened to meet global challenges. ©Photo: ©FAO/Ch. Errath |
|
| Posted: 2021-06-30 | More... |
Sharing useful national tree species database |
|
 |
|
| Posted: 2021-03-15 | More... |
The state of the World’s Forests 2020 |
|
 |
|
| Posted: 2020-12-25 | More... |
SF Volume 3, Issue 1 is now live! |
|
We are pleased to announce that the Vol. 3, Issue 1 for 2020 of Sustainable Forest has been published, and is currently available for download. Click here to access the full issue. |
|
| Posted: 2020-06-30 | More... |
Meet our Editors-in-Chief |
|
Prof. Dmitry Ponomarev Prof. Leonor Calv |
|
| Posted: 2019-12-23 | More... |
SF Volume 2, Issue 1 is now live! |
|
We are pleased to announce that the Vol. 2, Issue 1 for 2019 of Sustainable Forest has been published, and is currently available for download. Click here to access the full issue. |
|
| Posted: 2019-06-30 | More... |
Call for papers |
|
Aims & Scope Sustainable Forestry (SF, eISSN: 2578-2002) is an open access, peer-reviewed journal publishing scientific research from any discipline that can provide interesting contributions about forest ecosystems and their sustainability. Innovative science as well as application-oriented work is welcomed. They could cover a broad spectrum of forest sciences including genetics, physiology, ecology, hydrology, meteorology, agroforestry, forest economics and policy, etc., all in relation to benign development of forest. |
|
| Posted: 2019-01-02 | More... |
Warming: Peatlands will store more carbon initially, but that will change |
|
Peatlands are extremely effective at storing carbon, but an international study featuring a University of Queensland researcher has found climate change could stop that. The group investigated how peatlands -- swamps and bogs with organic rich soils -- have responded to climate variability between 850 BCE and 1850 CE. Associate Professor Patrick Moss, from UQ's School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, believes the research is critical in understanding how climate affects the absorption properties of peatlands.  These are the peatlands of Moon Point on Queensland's Fraser Island. Credit: Patrick Moss |
|
| Posted: 2018-09-15 | More... |
In warming Arctic, major rivers show surprising changes in carbon chemistry |
|
Over the past several decades, the Arctic has begun to show signs of significant ecological upheaval. The rate of warming in the Arctic is nearly twice the global average, and those changes are triggering a cascade of destabilizing environmental effects. Ice is melting, permafrost is thawing, and experts say fires in Arctic forests are as damaging as they've been in 10,000 years. But new research suggests that the same factors driving the Arctic's changing climate are fueling a geological response that could play a small part in counteracting those changes' malign effects.  In two major arctic rivers, a changing climate and shifting human activities are having a surprising response. Credit: Norman Kuring, NASA |
|
| Posted: 2018-09-08 | More... |
Carbon reserves in Central American soils still affected by ancient Mayan deforestation |
|
Deforestation is suspected to have contributed to the mysterious collapse of Mayan civilization more than 1,000 years ago. A new study shows that the forest-clearing also decimated carbon reservoirs in the tropical soils of the Yucatan peninsula region long after ancient cities were abandoned and the forests grew back. The findings, published in the journal Nature Geoscience, underscore how important soils and our treatment of them could be in determining future levels of greenhouse gases in the planet's atmosphere.  This is an ancient stone carving of the Maya God Pauahtun, taken at Copan Ruinas, Honduras. Credit: Peter Douglas |
|
| Posted: 2018-08-23 | More... |
| 1 - 22 of 22 Items | |