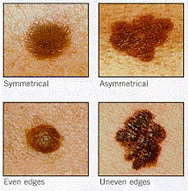
Most moles are not dangerous, but melanoma may look like moles, and some may develop from moles. If ultraviolet radiation is excessive, usually through long-term exposure over a lifetime, melanocytes may begin to grow uncontrolled. If there is indeed excessive radiation, melanocytes will become melanoma, usually in people with a genetic predisposition to this condition. Melanoma has the tendency to invade nearby tissues and then spread to the whole body through the blood or lymphatic system.
But how does melanoma come into being? Frances P. Noonan has indicated that cutaneous malignant melanoma may arise as a consequence of intense, intermittent exposure of the skin to ultraviolet radiation, particularly in children, rather than from the cumulative lifetime exposure that is associated with other forms of skin cancer. These results provide experimental support for epidemiological evidence that childhood sunburn poses a significant risk of developing this potentially fatal disease. Yamazaki F. used model animals to get the epidemiology of carcinogenesis by solar ultraviolet rays. With the rapid development of medicine in the world, many therapeutic methods, including molecular targeted drugs, have improved the prognosis of patients, Motonobu Nakamura briefly review the carcinogenic mechanism of malignant melanoma from the aspects of ultraviolet rays, mechanical stress, trauma and so on. For information, please click: https://systems.enpress-publisher.com/index.php/ti/article/view/1280
|