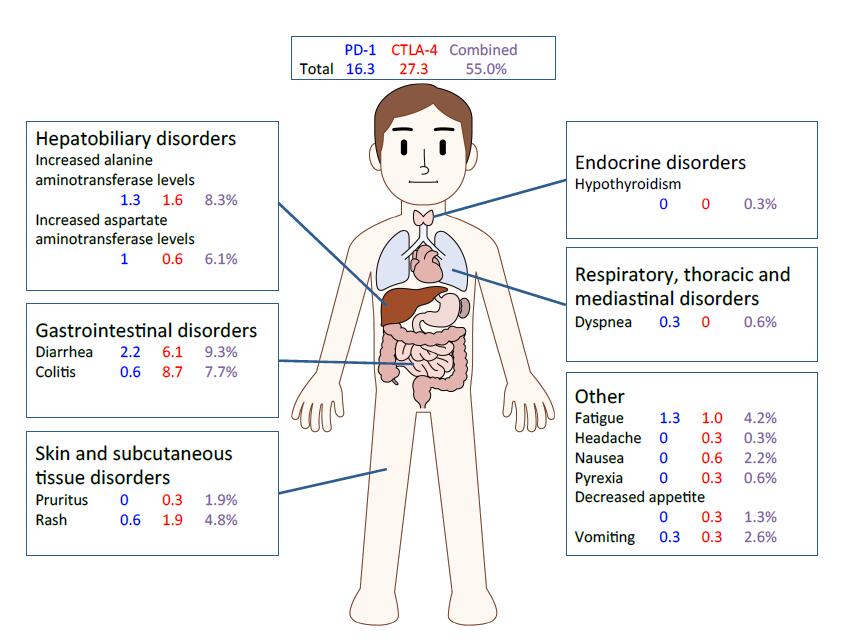
Table of Contents


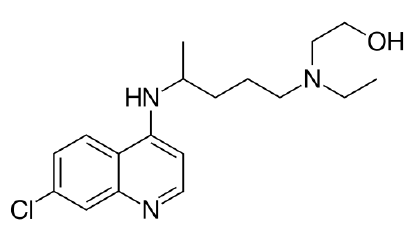
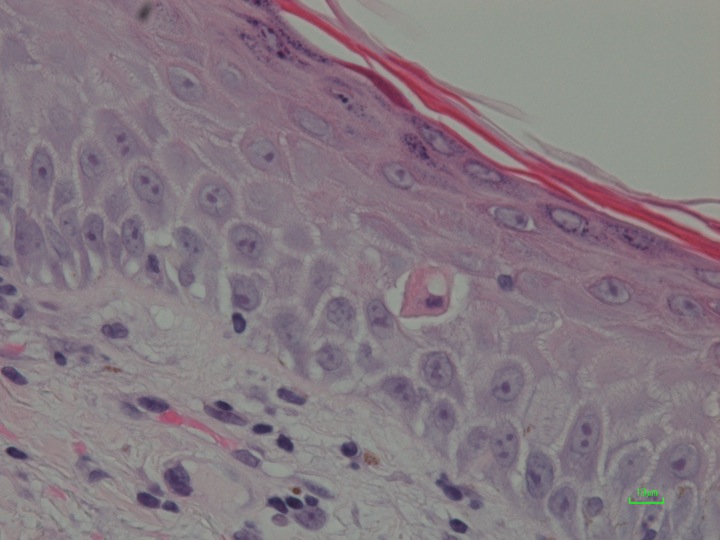
Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) is an autoimmune disorder that usually occurs on sun exposed areas. We describe a case of a 31-year-old man with reddish-purple, atrophic plaques on the nose and the bilateral cheeks. Histopathologic and direct immuneofluorescent studies confirmed DLE diagnosis. The skin lesion had been previously resistant to topical clobetasol propionate 0.05% and tacrolimus 0.1% since 2012, and were treated with oral hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) (300 mg daily). Two weeks later, the diarrhea happened frequently as side effects. Then, the dcreased HCQ 200 mg daily improved the diarrhea moderately. The patient who had a history of urticaria also complained about urticarial reaction much more frequently 3 weeks later more than the start, which was improved very much by epinastine (10 mg daily) administration. CLASI (cutaneous lupus erythematsus disease area and severity index) activity score improved from 11 to 5 for 3 months.














 Open Access
Open Access