What is the nanomaterial? Nanometer materials refer to materials whose structural unit sizes are in the range of 1 nanometer to 100 nanometers. This new type of material was discovered by scientists in the middle of the last century. Due to its unique size and structure, this new type of material has acquired unusual capabilities. 
Types of nanomaterials Nanomaterials cover a wide range and can be used in many fields. By material: Nano materials include nano metal materials, nano non-metal materials, nano polymer materials and nano composite materials. Among them, nano-non-metallic materials include nano-ceramic materials, nano-oxide materials and other non-metallic nano-materials. By function: Nano materials include nano biomaterials, nano magnetic materials, nano medicine materials, nano catalytic materials, nano smart materials, nano wave absorbing materials, nano heat sensitive materials, nano environmental protection materials, etc. The application of nanomaterials in medicine
Medical angiography Magnetic nanomaterials are the primary contrast agents used in magnetic resonance imaging to provide contrast and clarity. The magnetic nanomaterial is generally composed of ferroferric oxide with the size of 3-10nm or containing the element Gd, is harmless to a human body and can be better discharged out of the body through metabolism. The nano contrast agent can flow and circulate along with blood in the whole body, but it can be "absorbed" by the cancerous part, thus distinguishing the cancerous part from the normal part. biosensing Biosensors are mainly used to detect substances such as biological enzymes, nucleic acids, antigens, antibodies and bacteria. In recent years, functionalized nanomaterials have been used as biosensors to achieve high-sensitivity detection and substance recognition at the molecular level. Nanomaterial sensors can specifically recognize heavy metals, protein, antigens/antibodies, and various enzymes in cells with good detection range and very low detection limit. The biosensors prepared from nanomaterials can detect various tumor markers in biomedicine, providing sufficient evidence for the confirmation of diseases. Nano-drug loading Generally, the size of nano-materials is much smaller than that of normal cells. Therefore, using nano-materials as drug carriers into human body for drug delivery can control the drug release at specific sites. As drug carriers, nano-materials can realize targeted controlled release of drugs, and avoid the disadvantages of traditional drugs such as inaccuracy, low efficiency and short duration. New insights of nanomaterials in tumor diagnosis and treatment Recently, Professor Fan Xianqun's team has made important progress in the research on the development of tumor nano diagnostic reagents. It has been discovered for the first time in the study that the nanomaterials can increase the level of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Uvealmelanoma (UM) cells. ROS mediated by nanomaterials at different concentrations have different effects on the malignant growth ability of UM cells. A certain amount of ROS can activate the mTOR signaling pathway in UM cells and enhance amino acid metabolism. This study has very important reference value for the reasonable selection of safe concentration in the application of nanomaterials in tumor diagnosis and treatment. 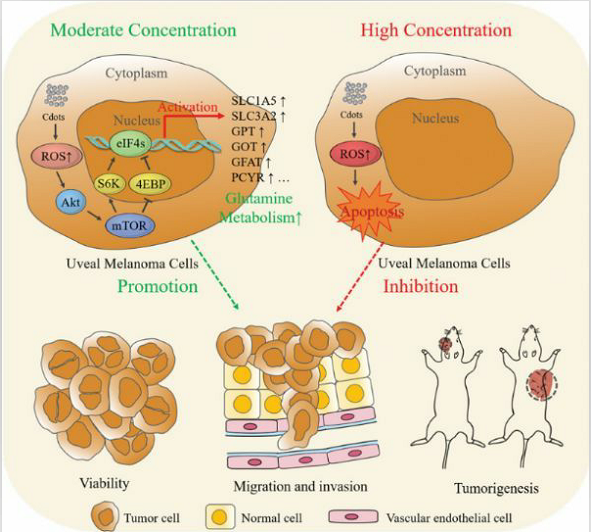 Source from:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?src=11×tamp=1630293474&ver=3283&signature=64HxN9ulYvltapK5q5SAAPuiEymII9dTB-BOfd-FFKBW14juBxE-NMf19Dgg6yLmIrX6NzpBQazzXEwaDLyZOkXqwNs2ZN6WEMJINkLWpodPBCLSwBpXPiSDoqhVmZ6h&new=1 Bioon.com. https://news.bioon.com/article/6787160.html Ding Y, Yu J, Chen X, Wang S, et al. Dose-Dependent Carbon-Dot-Induced ROS Promote Uveal Melanoma Cell Tumorigenicity via Activation of mTOR Signaling and Glutamine Metabolism. Advanced Science 2021, 8(8):2002404.
|


_1.jpg)


